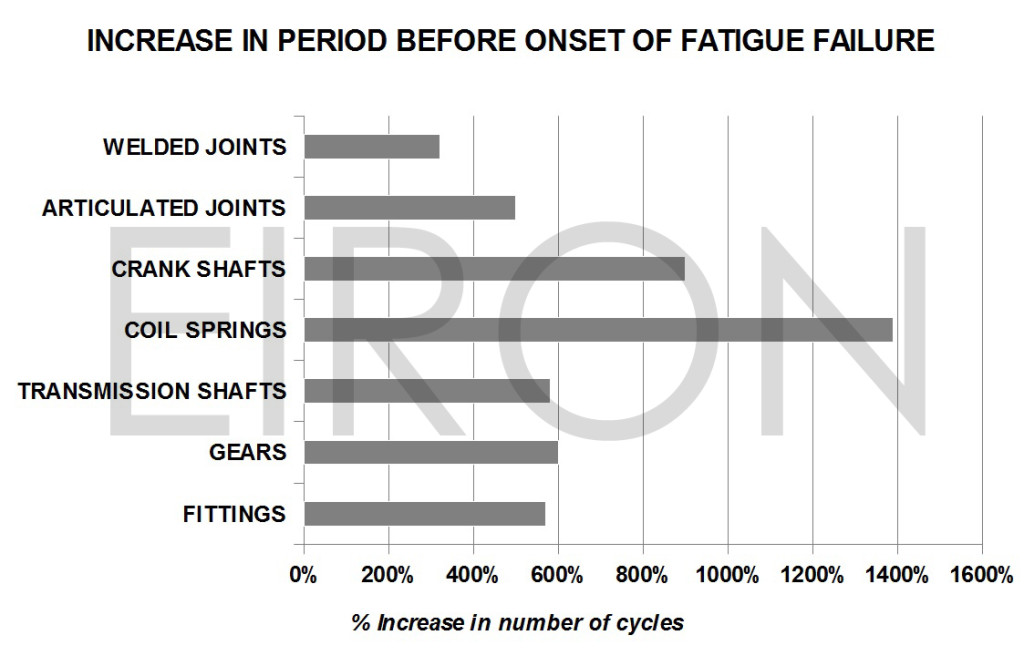
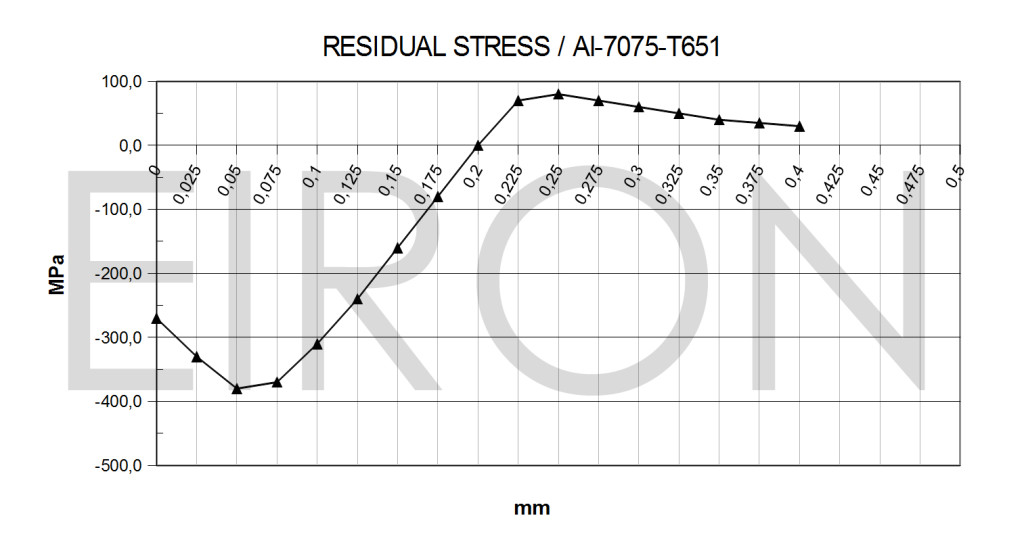
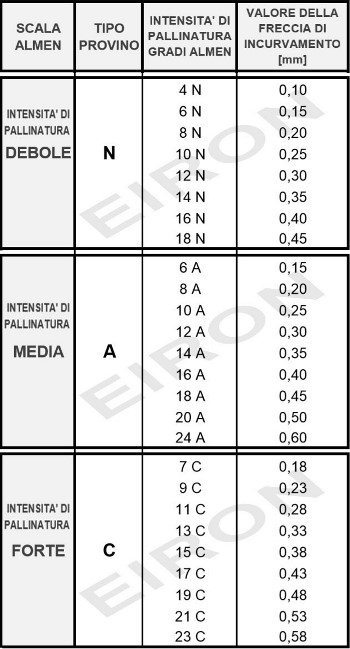
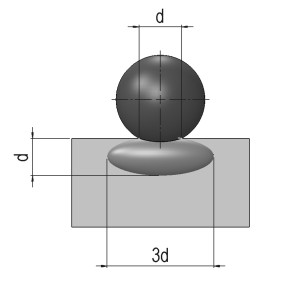
SHOT PEENINGShot peening is a mechanical process of cold treatment of the surfaces which must always be performed after thermal treatments. At the industrial level, the peening was introduced in the 19th century in order to increase the hardness and to modify the micro geomeric characteristics of metal parts. In 1940 J. O. Almen, an engineer from General Motors, studied the effects of shot peening on components of automobile engines and created a method to measure its effects (Almen Comparator/Almen Gage). In particular he became aware of amazing improvements in mechanical strength on the metal surfaces. For any further information please do not hesitate to contact us. |
|